The influencer marketing landscape is undergoing a seismic shift, a revolution powered by both human connection and algorithmic creation. For years, brands chased the elusive “influencer” – a person with a massive, often unattainable, following. But that paradigm is shattering. Two powerful, opposing forces are now defining the new frontier: the authentic, relatable power of micro-influencers and the perfectly scalable, controllable reality of AI-generated influencers.
This isn’t just a trend; it’s a fundamental reimagining of brand advocacy, audience trust, and marketing ROI. By 2025, the global influencer marketing industry is projected to surpass $24 billion, but how that budget is allocated is changing dramatically. Brands are faced with a critical strategic decision: invest in the genuine, community-driven credibility of micro-influencers or leverage the futuristic, data-driven efficiency of AI avatars.
This comprehensive analysis delves deep into this pivotal clash. We will dissect the strengths, weaknesses, and optimal use cases for both camps, providing data-driven insights to help you navigate the future of influencer marketing.
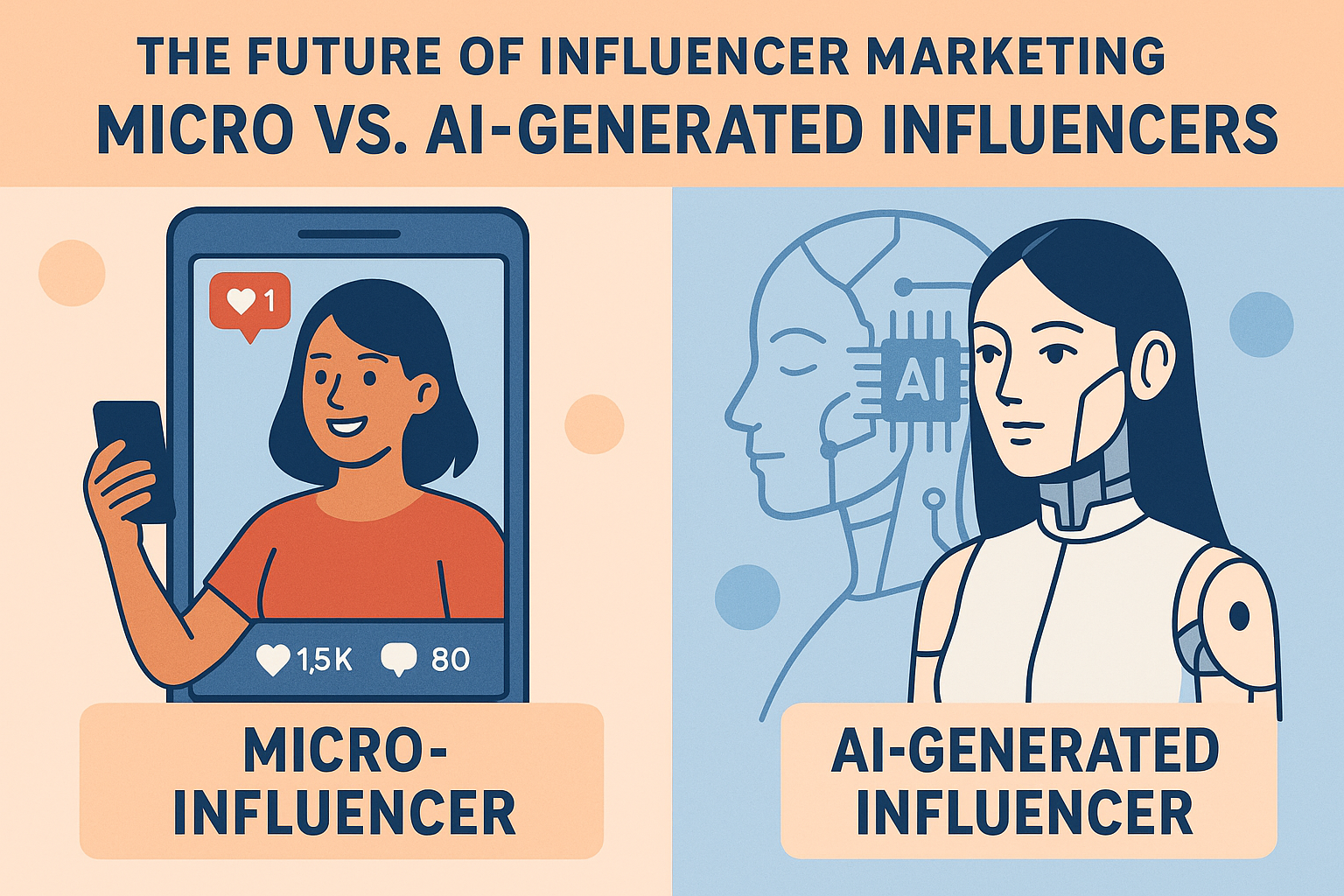
The Unstoppable Rise of the Micro-Influencer
Before we contrast them with AI, it’s crucial to understand what a micro-influencer is and why they have become the darling of performance-focused marketers.
Defining the Modern Micro-Influencer
A micro-influencer is typically defined as an individual with a highly engaged following between 1,000 and 100,000 followers. Their power does not lie in reach alone but in a deep, trusting relationship with a niche community. They are seen as peers, experts, or trusted friends rather than distant celebrities.
Why Micro-Influencers Deliver Unmatched ROI
The data consistently supports the value proposition of micro-influencers:
- Higher Engagement Rates: A 2024 report by Influencer Marketing Hub revealed that micro-influencers (1K-10K followers) boast an average engagement rate of 3.8%, compared to just 1.2% for mega-influencers (1M+ followers). This is the “trust dividend” in action.
- Authenticity and Credibility: Their content feels organic, not staged. A recommendation from a micro-influencer is perceived as a genuine endorsement, not a paid advertisement. This authenticity is their most valuable currency.
- Niche Audience Targeting: A micro-influencer in the sustainable fashion space, for example, has an audience that is specifically interested in that topic. This allows for hyper-targeted campaigns that speak directly to a converted audience.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Collaborating with a roster of micro-influencers is often more affordable than a single campaign with a macro-influencer, allowing for broader testing and diversification of strategy.
Case Study: Glossier and the Power of Community
Beauty brand Glossier famously built its initial empire almost exclusively through micro-influencer and user-generated content (UGC). Instead of hiring A-list celebrities, they empowered their customers—real people with real skin—to become their advocates. This strategy created a powerful sense of community and belonging, translating into immense brand loyalty and skyrocketing sales. It proved that trust, not just reach, drives conversion.
The Dawn of the AI-Generated Influencer
On the opposite end of the spectrum lies a phenomenon born not from community but from code. AI-generated influencers, or virtual influencers, are digital avatars created using computer graphics and artificial intelligence.
What Exactly is an AI-Generated Influencer?
These are photorealistic or stylized characters with unique personalities, backstories, and curated lifestyles. They “live” on social media platforms like Instagram and TikTok, posting content, interacting with followers, and partnering with brands. Their entire existence is orchestrated by a team of developers, designers, and writers, often enhanced by AI tools for content ideation and even voice synthesis.
The Alluring Advantages of AI Influencers
Brands are experimenting with virtual influencers for compelling reasons:
- Total Control and Brand Safety: There is no risk of a scandal, a controversial tweet, or a PR disaster. The brand has complete control over the avatar’s image, messaging, and behavior, mitigating a significant risk associated with human influencers.
- 24/7 Availability and Scalability: An AI influencer doesn’t get tired, sick, or demand time off. They can produce content, engage in multiple campaigns simultaneously, and be scaled across global markets without logistical nightmares.
- Perfect Brand Alignment: Every aspect of the virtual influencer—from their aesthetic to their values—can be perfectly tailored to embody a brand’s identity. They are the ultimate brand avatar.
- Pioneering the Metaverse: As digital worlds become more prominent, these AI entities are native citizens. They are perfectly positioned to lead brand activations in the metaverse, a frontier where human influencers have a less natural presence.
Case Study: Lil Miquela and the Virtual Vanguard
With over 3 million Instagram followers, Lil Miquela (@lilmiquela) is the archetype of a successful AI influencer. She has partnered with mega-brands like Prada, Calvin Klein, and Samsung. Her creators, Brud, have given her a complex narrative, even involving “relationships” with other virtual beings. While her engagement can be lower than a comparable human influencer’s, her value lies in generating massive press, buzz, and positioning partner brands as cutting-edge.
Head-to-Head: The Strategic Showdown
To determine the right strategy, we must pit these two forces against each other across key marketing dimensions.
| Dimension | Micro-Influencers (The Human Touch) | AI-Generated Influencers (The Algorithmic Edge) |
|---|---|---|
| Authenticity & Trust | High. Built on genuine human experience and relatability. | Low to Medium. Perceived as corporate creations, though some narratives can be engaging. |
| Engagement Quality | High. Comments and interactions are personal, emotional, and community-focused. | Variable. Often driven by novelty and curiosity. Interactions can feel scripted or superficial. |
| Scalability | Low to Medium. Requires managing multiple relationships. Difficult to scale instantly. | Extremely High. Can be deployed across countless campaigns and regions simultaneously. |
| Control & Brand Safety | Variable. Risk of human error, changing opinions, or PR issues. | Absolute. Complete control over message, aesthetic, and behavior. |
| Cost Structure | Variable. Can be cost-effective per influencer, but costs add up with volume. | High Initial Investment. Costly to create and maintain, but potentially lower long-term cost per post. |
| Niche Targeting | Precise. Experts in very specific verticals (e.g., vegan baking, miniature painting). | Broad. Can be designed for a niche, but often appeals to a wider, tech-savvy audience. |
| Metaverse Readiness | Low. Human presence in virtual worlds is still being defined. | Native. inherently digital, making them ideal pioneers for virtual brand experiences. |
The Hybrid Future: Convergence and Co-Creation
The most forward-thinking strategies won’t choose one over the other but will find ways to integrate both human and artificial intelligence. The future of influencer marketing is hybrid.
1. AI as an Empowerment Tool for Micro-Influencers
Micro-influencers are already using AI tools to enhance their own creativity and efficiency. This includes:
- Content Ideation: Using chatbots like ChatGPT to brainstorm campaign ideas or caption angles.
- Analytics and Strategy: Leveraging AI-powered platforms to analyze audience demographics and optimal posting times.
- Editing and Production: Utilizing AI-based video and photo editing tools to produce more polished content without a large budget.
In this model, AI doesn’t replace the influencer; it augments their human creativity, allowing them to compete with larger creators and deliver even greater value to brands.
2. Humanizing the AI: The Best of Both Worlds
The next generation of AI influencers will become more sophisticated, leveraging generative AI to become more “human.”
- Dynamic Storytelling: Instead of pre-scripted content, future AI influencers could use large language models to have unique, unscripted conversations with followers in comments or DMs, building a deeper sense of connection.
- Hyper-Personalization: AI influencers could analyze a user’s data (with consent) to deliver personalized shoutouts or product recommendations, creating a one-to-one marketing experience at scale.
3. Campaign-Specific Roles
The savvy brand will assign roles based on campaign objectives:
- Use Micro-Influencers for: Product launches requiring genuine reviews, building local community trust, and driving high-intent conversions through authentic testimonials.
- Use AI Influencers for: High-concept, fantastical campaigns that would be impossible for a human, global brand messaging that requires absolute consistency, and leading metaverse or gaming integrations.
Ethical Considerations and Future Challenges
This new landscape is not without its complexities.
- Transparency: Should brands be mandated to disclose partnerships with AI influencers clearly? The line between human and machine is blurring, raising questions about consumer deception.
- Unrealistic Beauty Standards: AI influencers often feature digitally perfected, impossible physiques, potentially exacerbating issues around body image and unrealistic expectations.
- Job Displacement: While AI may create new roles (avatar designers, AI wranglers), there is a valid concern about the impact on human content creators and models.
- Data Privacy: The AI models that power these virtual beings require vast amounts of data. How this data is collected and used will be a critical area for scrutiny and regulation.
Conclusion: The Human Heart Still Beats
The future of influencer marketing is not a simple binary choice. It is a spectrum where micro-influencers represent the enduring power of human authenticity, trust, and community, while AI-generated influencers represent the formidable potential of scalability, control, and digital innovation.
For brands seeking to build genuine, long-term loyalty and drive conversions through trusted recommendations, the human touch of micro-influencers remains arguably the most powerful tool. However, for brands aiming to generate massive buzz, execute flawless global campaigns, and establish a foothold in digital futures, AI influencers offer a compelling and innovative avenue.
The winning strategy will be agile, empathetic, and technologically savvy. It will involve a portfolio approach that leverages the relatable authenticity of humans for depth and the flawless efficiency of AI for scale. Ultimately, technology is the tool, but human connection remains the goal.
Ready to refine your influencer marketing strategy? Start by auditing your past campaigns. Identify whether your goals are better aligned with building authentic community or generating scalable brand awareness. Your objective will point you toward the right blend of human and AI influence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can AI-generated influencers truly build a loyal community like humans can?
A: While they can attract a large following based on novelty and aesthetic, building deep, emotional loyalty is challenging. Their interactions are programmed, lacking the genuine shared experiences and empathy that form the core of human-led communities. However, as AI becomes more advanced, the line will continue to blur.
Q2: What is the typical cost difference between a micro-influencer and an AI influencer campaign?
A: Collaborating with a single micro-influencer is generally less expensive upfront. However, a campaign using 20-30 micro-influencers can have a similar total cost to licensing an existing AI influencer for a campaign. Creating a custom AI influencer from scratch involves a significant initial investment (often $50,000+) for design, modeling, and narrative development.
Q3: How can consumers tell if an influencer is real or AI-generated?
A: Look for subtle tells: perfectly flawless skin and features, a slightly uncanny valley appearance, inconsistent physics in videos (hair, clothing), and a bio that may be vague or fantastical. However, the technology is improving so rapidly that soon, it may be nearly impossible to tell without a disclosure.
Q4: Are there any regulations governing the use of AI influencers?
A: Regulation is currently lagging behind technology. The FTC guidelines in the U.S. require clear disclosure of sponsored content, but it’s an open debate whether an AI influencer itself is a “sponsorship.” The UK’s Advertising Standards Authority (ASA) has already ruled that ads featuring AI influencers must be obviously identifiable as marketing. More comprehensive global regulations are expected in the coming years.
Q5: Which approach provides a better return on investment (ROI)?
A: There is no one-size-fits-all answer. Micro-influencers often deliver a higher ROI for direct response campaigns (e.g., using discount codes) due to their high trust and conversion rates. AI influencers can deliver a superior ROI for top-of-funnel brand awareness and buzz generation, where metrics like impressions and media value are key. The ROI depends entirely on the campaign’s primary goal.