As artificial intelligence, IoT devices, and real-time applications reshape the American business landscape, the computing infrastructure powering these innovations stands at a critical crossroads.
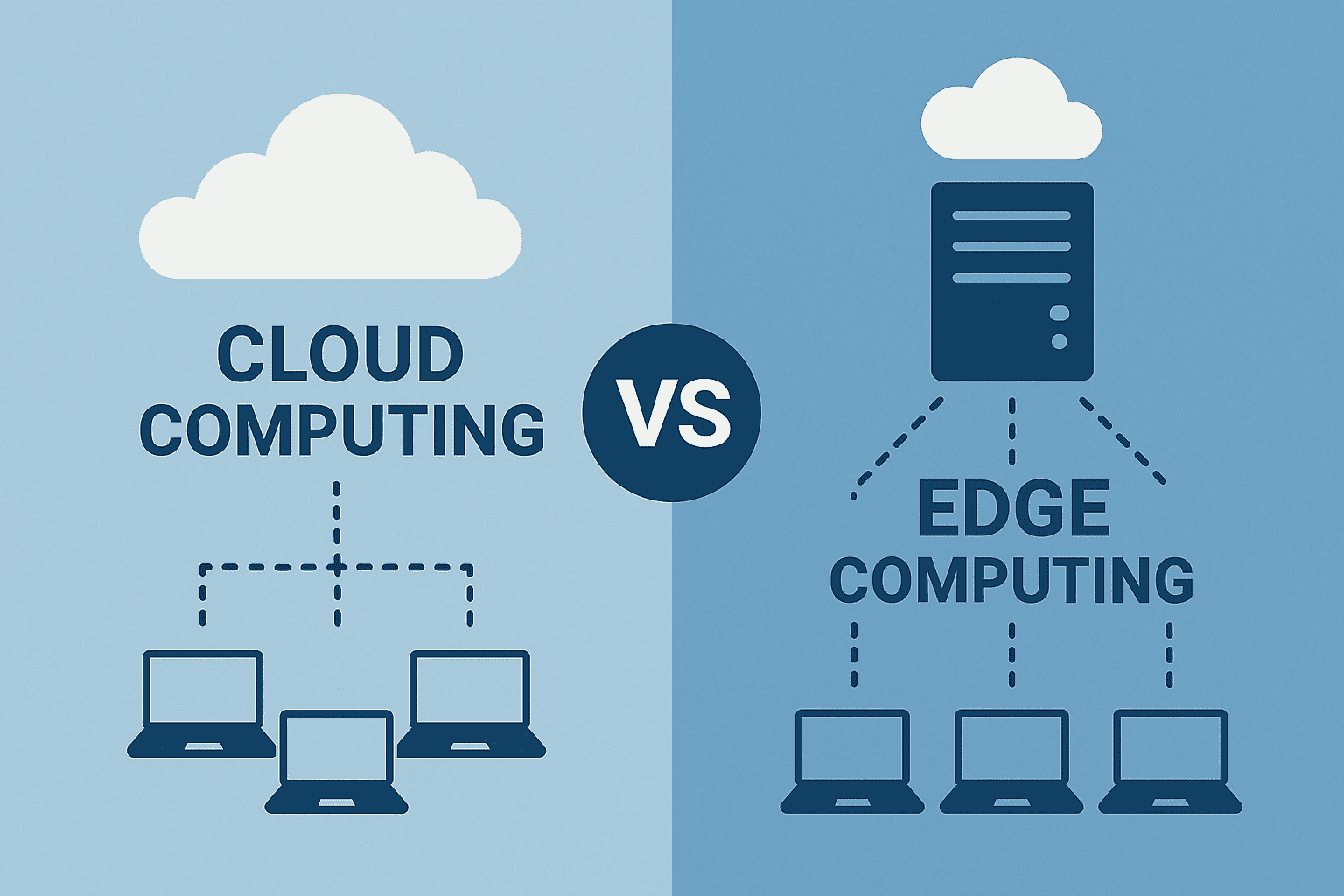
The digital transformation sweeping across the United States has reached an inflection point. While cloud computing has been the undisputed champion of enterprise technology for nearly two decades, a new contender is rapidly gaining ground: edge computing. This technological rivalry isn’t just about processing power—it’s about determining how American businesses, from Silicon Valley startups to Fortune 500 corporations, will compete in an increasingly data-driven economy.
Recent market research indicates that the global edge computing market is projected to explode from $53.6 billion in 2024 to a staggering $232.9 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.1%. Meanwhile, the cloud computing market, valued at $626.4 billion in 2023, continues its steady ascent toward $1.44 trillion by 2029. The question isn’t whether one will eliminate the other, but rather how their convergence will redefine American technological supremacy.
The Cloud Computing Revolution: America’s Digital Backbone
How Cloud Technology Transformed American Business
Since Amazon Web Services (AWS) launched in 2006, cloud computing has fundamentally transformed how American businesses operate, compete, and scale. The technology shifted the paradigm from capital-intensive on-premises infrastructure to flexible, scalable, and cost-effective cloud-based solutions.
Today’s cloud computing landscape is dominated by American giants:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) commands approximately 32% of the global market share
- Microsoft Azure holds roughly 23% of the worldwide cloud infrastructure market
- Google Cloud Platform captures about 11% of global cloud services revenue
The impact on American businesses has been revolutionary. Netflix transformed from a DVD-by-mail service to a global streaming giant by leveraging AWS’s scalability. Airbnb built its entire marketplace on cloud infrastructure, enabling rapid international expansion without massive infrastructure investments. Slack revolutionized workplace communication by utilizing cloud-native architecture to serve millions of users worldwide.
Key Advantages Driving Cloud Adoption
Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud computing enables American businesses to scale resources up or down instantly based on demand. During the COVID-19 pandemic, companies like Zoom scaled their infrastructure to accommodate a 30x increase in usage within weeks—a feat impossible with traditional on-premises systems.
Cost Optimization: The pay-as-you-go model has democratized access to enterprise-grade technology. Small American startups can now access the same computing resources as Fortune 500 companies, paying only for what they use. This has fueled innovation across sectors, from fintech to healthcare technology.
Global Reach and Accessibility: Major cloud providers operate data centers across the United States and globally, enabling American companies to deliver services worldwide with minimal latency. Companies like Spotify and Pinterest leverage this global infrastructure to serve international markets seamlessly.
AI and Machine Learning Integration: Cloud platforms have become the backbone of America’s AI revolution. Companies like OpenAI rely on cloud infrastructure to train and deploy large language models, while businesses across industries use cloud-based AI services for everything from fraud detection to personalized marketing.
The Cloud Computing Market Landscape in America
According to recent industry reports, 94% of American enterprises now use cloud services in some capacity. The adoption rates vary by industry:
- Technology sector: 98% cloud adoption rate
- Financial services: 89% adoption rate
- Healthcare: 83% adoption rate (growing rapidly due to telehealth expansion)
- Manufacturing: 76% adoption rate (increasing due to Industry 4.0 initiatives)
The economic impact is substantial. Cloud computing contributes an estimated $214 billion annually to the U.S. economy and supports over 2.3 million American jobs across various sectors.
Edge Computing: The Emerging Game-Changer
Understanding Edge Computing’s Revolutionary Approach
While cloud computing centralizes processing in distant data centers, edge computing brings computation closer to where data is generated and consumed. This distributed approach processes information at the “edge” of the network—whether that’s a smart factory in Detroit, a 5G cell tower in Los Angeles, or an autonomous vehicle navigating Manhattan traffic.
The technology represents a fundamental shift in thinking about data processing and application delivery. Instead of sending all data to centralized cloud servers for processing, edge computing enables real-time decision-making at the source, dramatically reducing latency and improving application performance.
The American Edge Computing Boom
The United States is leading the global edge computing revolution, driven by several converging trends:
5G Network Deployment: Major American carriers including Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile have invested over $100 billion in 5G infrastructure. This ultra-fast, low-latency network technology is the foundation enabling edge computing applications across industries.
IoT Explosion: American businesses are deploying Internet of Things (IoT) devices at an unprecedented scale. Manufacturing companies are implementing smart factory initiatives, cities are deploying intelligent traffic systems, and healthcare providers are using connected medical devices for remote patient monitoring.
Autonomous Vehicle Development: Companies like Tesla, Waymo (Alphabet), and Cruise (General Motors) are pioneering autonomous driving technology that requires split-second decision-making capabilities—impossible to achieve with cloud-only architectures.
Critical Advantages of Edge Computing
Ultra-Low Latency Performance: Edge computing reduces data processing latency from hundreds of milliseconds (cloud) to single-digit milliseconds (edge). This performance improvement is critical for applications requiring real-time responses, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and augmented reality experiences.
Bandwidth Optimization and Cost Reduction: By processing data locally and sending only relevant insights to the cloud, edge computing dramatically reduces bandwidth usage and associated costs. A smart factory might generate terabytes of sensor data daily but only needs to send summarized analytics to cloud-based management systems.
Enhanced Data Privacy and Security: Edge computing enables sensitive data to remain local, addressing privacy concerns and regulatory compliance requirements. Healthcare providers can process patient data locally while maintaining HIPAA compliance, and financial institutions can perform fraud detection without transmitting sensitive transaction data to external clouds.
Improved Reliability and Resilience: Edge systems continue operating even when cloud connectivity is disrupted. This resilience is crucial for mission-critical applications in manufacturing, transportation, and emergency services.
Industry-Specific Applications: Where Each Technology Excels
Cloud Computing Dominance Sectors
Enterprise Software and SaaS Applications: Cloud computing remains the optimal choice for software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications used by American businesses. Companies like Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, and Slack leverage cloud infrastructure to serve millions of users globally with consistent performance and reliability.
Big Data Analytics and Business Intelligence: American companies process massive datasets for business insights using cloud-based analytics platforms. Retailers analyze customer behavior patterns, financial institutions detect fraudulent transactions, and healthcare organizations identify treatment effectiveness across large patient populations.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Training: Training sophisticated AI models requires enormous computational resources best provided by cloud platforms. Companies like OpenAI, Google, and Meta use cloud infrastructure to train large language models and computer vision systems that power today’s AI applications.
Content Delivery and Media Streaming: American media companies including Netflix, Disney+, and Amazon Prime Video rely on cloud-based content delivery networks (CDNs) to stream high-quality video content to millions of users worldwide.
Edge Computing Excellence Areas
Autonomous Vehicle Technology: American automotive companies and tech giants are investing billions in self-driving car technology. Tesla’s Full Self-Driving system, Waymo’s autonomous taxi service, and GM’s Cruise platform all rely on edge computing to process sensor data and make split-second driving decisions without cloud connectivity delays.
Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0: American manufacturers are embracing edge computing to optimize production processes. General Electric uses edge analytics in jet engines to predict maintenance needs, while Ford employs edge computing for real-time quality control in vehicle assembly lines.
Healthcare and Telemedicine: The American healthcare system increasingly relies on edge computing for critical applications. Remote surgery systems require ultra-low latency for precise control, while wearable medical devices use edge processing for real-time health monitoring and emergency response.
Smart City Infrastructure: Cities across America are deploying edge computing for intelligent traffic management, public safety systems, and environmental monitoring. Los Angeles uses edge-enabled traffic signals to optimize traffic flow, while New York City employs edge computing for real-time security surveillance and incident response.
Retail and Customer Experience: American retailers leverage edge computing to enhance in-store experiences. Walmart uses edge analytics for inventory management and checkout optimization, while Amazon Go stores rely on edge processing for cashier-less shopping experiences.
The Hybrid Future: Cloud-Edge Integration
The Convergence Revolution
Rather than competing technologies, cloud and edge computing are increasingly viewed as complementary components of a comprehensive digital infrastructure strategy. This hybrid approach, often called the “cloud-edge continuum,” enables American businesses to optimize performance, costs, and user experiences by processing data at the most appropriate location.
Leading American technology companies are already implementing integrated cloud-edge strategies:
Amazon’s Comprehensive Approach: AWS offers edge services including AWS Wavelength (ultra-low latency applications), AWS Outposts (on-premises cloud services), and AWS IoT Greengrass (edge computing for IoT devices). This integrated ecosystem allows businesses to seamlessly distribute workloads across cloud and edge environments.
Microsoft’s Intelligent Edge Strategy: Azure Edge Zones bring cloud services closer to users, while Azure IoT Edge enables cloud intelligence deployment on edge devices. Microsoft’s approach focuses on creating a unified development and management experience across cloud and edge environments.
Google’s Distributed Cloud Vision: Google Cloud offers Anthos for edge computing, enabling consistent application deployment across cloud and edge locations. The company’s distributed cloud approach aims to bring Google Cloud services to any location where businesses need them.
Real-World Hybrid Implementation Examples
Smart Factory Operations: A typical American manufacturing facility might use edge computing for real-time machine monitoring and quality control, while leveraging cloud computing for supply chain optimization and predictive maintenance analytics. This hybrid approach ensures immediate response to production issues while enabling long-term operational improvements.
Healthcare System Integration: Hospitals use edge computing for real-time patient monitoring and emergency response systems, while cloud computing handles electronic health record management, medical imaging storage, and population health analytics. This combination ensures patient safety while enabling healthcare system efficiency.
Autonomous Vehicle Ecosystem: Self-driving cars use edge computing for immediate driving decisions and safety systems, while cloud computing handles route optimization, traffic pattern analysis, and over-the-air software updates. This hybrid approach enables safe autonomous operation while continuously improving system performance.
Market Dynamics and Economic Impact
Investment and Market Growth Trends
The American technology sector is experiencing unprecedented investment in both cloud and edge computing technologies:
Cloud Computing Investment: Major cloud providers are investing billions in data center expansion across the United States. Amazon plans to invest $35 billion in Virginia data centers by 2040, while Microsoft committed $10 billion to expand cloud infrastructure nationwide. Google announced $13 billion in data center investments across multiple states.
Edge Computing Investment: Edge computing investments are accelerating rapidly. Verizon invested $10 billion in edge computing infrastructure development, while AT&T allocated $6 billion for edge and 5G network expansion. Private equity firms have invested over $15 billion in edge computing startups since 2022.
Economic Multiplier Effects: These investments create significant economic ripple effects across American communities. Cloud and edge computing infrastructure projects generate construction jobs, ongoing operational employment, and attract secondary businesses to surrounding areas.
Job Creation and Workforce Development
The cloud and edge computing revolution is creating new career opportunities across America:
High-Demand Technical Roles: Cloud architects, edge computing engineers, and DevOps specialists are among the fastest-growing technology positions. Average salaries for these roles range from $120,000 to $200,000 annually, with senior positions commanding even higher compensation.
Geographic Distribution: While Silicon Valley remains a technology hub, cloud and edge computing jobs are distributed across the United States. Major cloud data centers in Virginia, Ohio, and Texas create local employment opportunities, while edge computing initiatives span urban and rural areas nationwide.
Skill Development Initiatives: American universities and training organizations are rapidly expanding cloud and edge computing curricula. Amazon’s Cloud Career Choice program, Microsoft’s Skills Initiative, and Google’s Career Certificates are helping American workers transition into high-paying technology roles.
Challenges and Considerations
Cloud Computing Challenges
Data Security and Privacy Concerns: As American businesses store increasing amounts of sensitive data in cloud systems, security risks multiply. High-profile data breaches at major cloud providers have raised concerns about centralized data storage vulnerabilities. Companies must balance cloud convenience with data protection requirements.
Regulatory Compliance Complexity: American businesses operating in regulated industries face challenges ensuring cloud deployments meet compliance requirements. Healthcare organizations must maintain HIPAA compliance, financial institutions must adhere to SOX regulations, and government contractors must meet FedRAMP standards.
Vendor Lock-in Risks: Many American businesses worry about becoming overly dependent on specific cloud providers. Switching between AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud can be complex and expensive, potentially limiting future flexibility and negotiating power.
Cost Management Difficulties: While cloud computing offers cost flexibility, many American businesses struggle with cost management. Unexpected usage spikes, complex pricing structures, and hidden fees can result in budget overruns that impact profitability.
Edge Computing Challenges
Infrastructure Complexity: Managing distributed edge computing infrastructure is significantly more complex than centralized cloud systems. American businesses must coordinate security, updates, and maintenance across numerous edge locations, requiring specialized expertise and management tools.
Security at Scale: Edge computing creates multiple potential security vulnerabilities that must be individually secured and monitored. Each edge device represents a potential entry point for cyberattacks, multiplying security management requirements.
Standardization and Interoperability: The edge computing industry lacks standardized protocols and interfaces, making it difficult for American businesses to implement multi-vendor edge solutions. This fragmentation can limit flexibility and increase implementation costs.
Skilled Workforce Shortage: Edge computing requires specialized skills that are currently in short supply. American businesses struggle to find qualified edge computing engineers, creating talent competition and wage inflation in this emerging field.
Industry Predictions and Future Outlook
Technology Evolution Trajectories
5G and Beyond: The continued rollout of 5G networks across America will accelerate edge computing adoption by providing the high-bandwidth, low-latency connectivity necessary for advanced edge applications. Looking ahead, 6G technology development promises even greater edge computing capabilities.
Artificial Intelligence Integration: Edge AI chips and processing capabilities are rapidly advancing, enabling sophisticated machine learning models to run on edge devices. This trend will expand edge computing applications in autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation.
Quantum Computing Impact: While still emerging, quantum computing could revolutionize both cloud and edge computing paradigms. American companies like IBM, Google, and startups like Rigetti are developing quantum technologies that could provide unprecedented processing capabilities.
Market Consolidation Trends
Strategic Acquisitions: Major technology companies are acquiring edge computing specialists to expand their capabilities. Recent acquisitions include VMware’s purchase of VeloCloud and Cisco’s acquisition of edge computing startups to strengthen their hybrid cloud-edge offerings.
Partnership Ecosystem Development: Cloud providers are forming strategic partnerships with telecommunications companies, hardware manufacturers, and software developers to create comprehensive edge computing ecosystems. These partnerships aim to simplify edge deployment and management for American businesses.
Industry Standardization Efforts: Organizations like the Industrial Internet Consortium and Edge Computing Consortium are working to establish industry standards that will improve interoperability and reduce deployment complexity for American businesses.
Strategic Recommendations for American Businesses
Assessment and Planning Framework
Infrastructure Audit: American businesses should conduct comprehensive assessments of their current computing infrastructure, identifying applications that would benefit from cloud migration versus those requiring edge processing capabilities.
Use Case Prioritization: Companies should prioritize cloud and edge computing investments based on business impact and technical requirements. Real-time applications with strict latency requirements are ideal for edge computing, while scalable analytics and storage applications are better suited for cloud platforms.
Hybrid Strategy Development: Rather than choosing between cloud or edge computing, American businesses should develop integrated strategies that leverage both technologies optimally. This approach maximizes performance while minimizing costs and complexity.
Implementation Best Practices
Pilot Project Approach: Companies should start with small-scale pilot projects to test cloud and edge computing technologies before large-scale deployments. This approach reduces risk while enabling organizations to develop expertise and best practices.
Vendor Evaluation: Businesses should carefully evaluate cloud and edge computing vendors based on technical capabilities, pricing models, support quality, and long-term viability. Multi-vendor strategies can reduce dependency risks while optimizing performance and costs.
Security-First Design: All cloud and edge computing implementations should prioritize security from the initial design phase. This includes encryption, access controls, monitoring, and incident response capabilities across all deployment environments.
Workforce Development Strategies
Skill Gap Analysis: Organizations should assess current employee skills and identify training needs for cloud and edge computing technologies. This analysis should inform recruitment and professional development strategies.
Training and Certification Programs: Companies should invest in employee training programs and industry certifications from major cloud providers. These investments improve employee capabilities while demonstrating commitment to professional development.
Partnership with Educational Institutions: American businesses should partner with local colleges and universities to develop cloud and edge computing curricula that meet industry needs. These partnerships help ensure future workforce availability while supporting community development.
The Verdict: A Distributed Computing Future
Beyond the Cloud vs. Edge Debate
The question of whether cloud or edge computing will dominate the next decade reflects outdated thinking. The future belongs to distributed computing architectures that seamlessly integrate cloud and edge capabilities to optimize performance, cost, and user experience.
American businesses that embrace this hybrid approach will gain competitive advantages through:
- Optimized Performance: Processing data at the most appropriate location for each use case
- Cost Efficiency: Balancing cloud scalability with edge processing to minimize overall costs
- Enhanced User Experience: Delivering fast, reliable applications that meet customer expectations
- Improved Security: Implementing defense-in-depth strategies across distributed infrastructure
- Greater Flexibility: Adapting quickly to changing business requirements and technology innovations
Industry Transformation Acceleration
The convergence of cloud and edge computing is accelerating transformation across American industries:
Healthcare: Telemedicine, remote surgery, and personalized medicine will rely on hybrid cloud-edge architectures to deliver life-saving care while protecting patient privacy.
Transportation: Autonomous vehicles, smart traffic systems, and logistics optimization will require seamless integration of edge processing for real-time decisions and cloud analytics for system-wide optimization.
Manufacturing: Industry 4.0 initiatives will leverage edge computing for production optimization and cloud platforms for supply chain management and business intelligence.
Retail: Personalized shopping experiences will combine edge computing for real-time recommendations with cloud analytics for inventory management and customer insights.
Financial Services: Fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and personalized banking will utilize edge processing for immediate responses and cloud computing for risk analysis and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion: Embracing America’s Distributed Computing Future
The debate between cloud and edge computing misses the fundamental point: the future is distributed. American businesses that recognize this reality and develop comprehensive strategies integrating both technologies will thrive in the digital economy of the 2020s and beyond.
The numbers tell the story: with edge computing markets growing at 27% annually and cloud computing maintaining steady expansion, the combined market opportunity represents over $1.6 trillion by 2030. American companies that position themselves at the forefront of this distributed computing revolution will capture the largest share of this massive market opportunity.
Success requires moving beyond traditional technology silos to embrace hybrid architectures that optimize performance, cost, and user experience. The companies that master this integration—leveraging cloud computing’s scalability and cost-effectiveness with edge computing’s speed and responsiveness—will define the next chapter of American technological leadership.
The future isn’t about choosing between cloud and edge computing. It’s about creating intelligent, distributed systems that process data wherever it makes the most sense, delivering unprecedented capabilities to American businesses and consumers alike. The organizations that understand and implement this vision will not just survive the digital transformation—they will lead it.
For more insights on cloud computing trends, visit the Cloud Security Alliance and the Edge Computing Consortium. Stay updated on the latest technology developments through MIT Technology Review and IEEE Computer Society.